site_4bbb466c-cafd-4edb-8869-71ed8e60d33a
Excellence in PGR technology
Effective Gibberellic Acid Application Techniques for Maximum Plant Growth
Gibberellic acid application has emerged as a transformative technique in promoting plant growth and improving crop yields. This growth hormone, derived from the fungus *Gibberella fujikuroi*, plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes within plants, including seed germination, stem elongation, and flowering. As agricultural practices evolve, understanding the most effective methods for gibberellic acid application is vital for farmers and horticulturists aiming to maximize their production potential.
Renowned plant physiologist Dr. Emily Turner emphasizes the significance of precision in gibberellic acid application, stating, "The key to unlocking the full potential of gibberellic acid lies in its timing and method of application." This highlights the necessity for growers to adopt a strategic approach, ensuring that the timing, concentration, and method align with the specific developmental stages of the plants they are nurturing. Whether through foliar sprays, soil drenches, or seed treatments, the effectiveness of gibberellic acid application is contingent on adhering to best practices that enhance its efficacy while minimizing potential drawbacks.
As research into gibberellic acid continues to advance, exploring innovative application techniques will remain essential. This introduction will delve into various effective methods and strategies that can be employed to optimize the benefits of gibberellic acid, ultimately fostering a more productive and sustainable agricultural future.
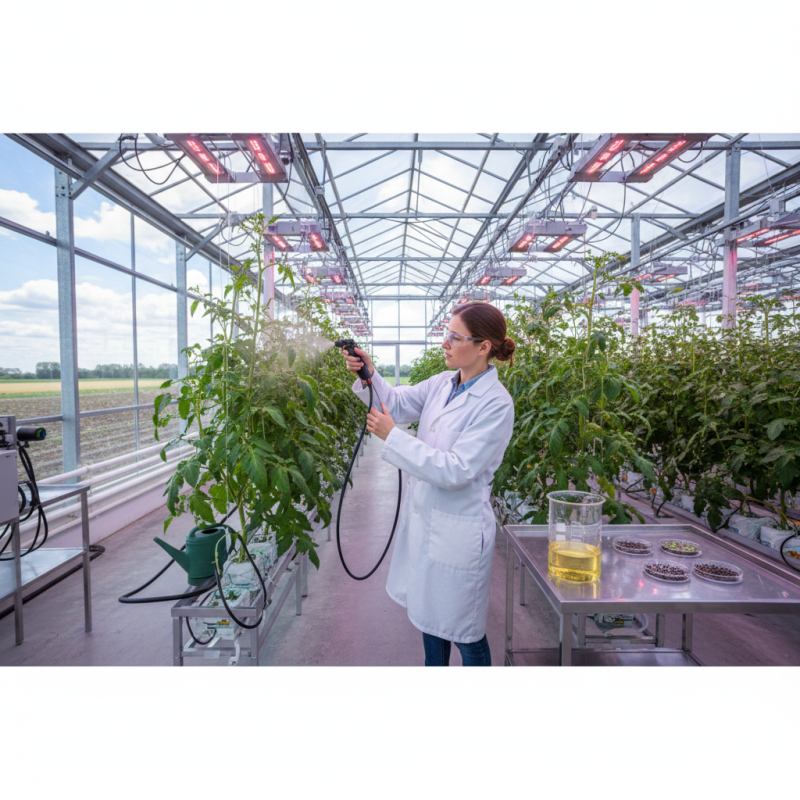

Understanding Gibberellic Acid and Its Role in Plant Growth
Gibberellic acid (GA) is a crucial plant hormone that significantly influences various growth processes, including seed germination, stem elongation, and flowering. This naturally occurring compound, derived from the fungus Gibberella fujikuroi, plays a vital role in stimulating cell division and elongation. Its application can lead to increased plant height, enhanced fruit size, and improved overall vigor, making it a valuable tool for horticulturists and agriculturalists seeking to maximize growth potential.
Understanding the mechanisms of gibberellic acid allows for more effective application strategies. GA promotes the breakdown of starches and other storage materials, which supports energy availability during critical growth phases. The timing and concentration of GA application are essential; for instance, applying it at the right stage of growth can significantly impact flowering and yield. Furthermore, environmental factors such as temperature and moisture levels can affect the hormone’s efficacy, emphasizing the need for tailored application techniques that account for specific plant needs and growth conditions.
Effective Gibberellic Acid Application Techniques for Maximum Plant Growth
| Application Technique | Concentration (g/L) | Timing | Plant Type | Expected Growth Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foliar Spray | 5-10 | Early Growth Stage | Vegetables | Increased Leaf Area |
| Soil Drench | 2-4 | Transplanting | Fruits | Enhanced Root Development |
| Seed Treatment | 1-3 | Before Sowing | Grains | Improved Germination Rate |
| Micro-injection | 10-15 | During Active Growth | Trees | Accelerated Height Growth |
| Aqueous Solution Bath | 0.1-0.5 | Pre-planting | Ornamentals | Vigorous Foliage Growth |
Optimal Concentrations of Gibberellic Acid for Different Plant Species

Gibberellic Acid (GA) is a crucial plant growth regulator that enhances various developmental processes in plants, such as seed germination, stem elongation, and flowering. However, to achieve optimal results, understanding the ideal concentrations of GA for different plant species is essential. For instance, common garden plants like tomatoes may respond well to GA concentrations around 50-100 ppm, while trees and shrubs might require slightly higher doses for effective growth promotion.
Tips: When applying GA, always conduct a small-scale trial to determine the best concentration for your specific plants. Over-application can lead to undesirable effects, such as excessive stretch or poor fruit set.
In addition, the timing of application plays a vital role in maximizing the benefits of GA. For many species, applying GA during the early stages of growth, such as before the flowering phase, can lead to enhanced yields and overall plant health. It is important to monitor the response and adjust concentrations accordingly, as various factors like plant health, soil conditions, and environmental factors can influence how plants react to GA.
Tips: Regularly check your plants for signs of stress or overgrowth after GA application. This will help you fine-tune future applications and ensure that your plants thrive without compromising their natural growth patterns.
Application Methods: Foliar Spraying vs. Soil Drench Techniques
When applying gibberellic acid (GA), two primary methods stand out:
foliar spraying and soil drench.
Foliar spraying involves applying the growth regulator directly onto the leaves of the plants, allowing for
quick absorption through the leaf surface. This method is particularly beneficial for eliciting rapid responses in
plant growth, as the foliage can readily take up the GA, leading to an immediate enhancement in growth rates,
flowering, and fruit set. For best results, it is important to spray during the early morning or late afternoon
when stomata are open, optimizing the absorption process.
On the other hand, soil drench techniques involve applying gibberellic acid
solution directly to the soil. This method promotes root uptake, allowing for a more sustained release of
growth hormones in the plant system. It is particularly advantageous for plants that may be experiencing
stress or where foliar application could lead to potential leaf burn. Soil drenching typically results in more
uniform growth, as the roots can absorb the GA over time. Both methods can be effective, but the choice
between them should be made based on the specific growth requirements of the plants involved and
environmental conditions.
Timing and Frequency of Gibberellic Acid Application for Best Results
The timing and frequency of Gibberellic Acid (GA) application are crucial factors in optimizing plant growth. To achieve the best results, it is essential to apply GA during key growth stages. For many plants, early application during the seedling stage can promote elongation and stronger development, enhancing overall vigor. Additionally, a follow-up treatment during flowering can significantly improve fruit set and yield. Adjusting the timing based on the specific growth patterns and climatic conditions of your plants ensures that GA works effectively.
When it comes to frequency, it’s vital to strike a balance. Over-application can lead to excessive growth or even inhibit certain developmental processes. Generally, a staggered application every two to four weeks can maintain an optimal growth rhythm without overwhelming the plants. Observing the plants’ response after each application will provide insights into their needs, allowing for adjustments in the schedule.
**Tip:** Always monitor environmental factors such as temperature and humidity, as these can impact how plants respond to GA.
**Tip:** Conduct small-scale trials with different timings to determine the most effective application strategy for your specific plants and conditions. This will help you refine your approach and maximize your results.
Monitoring Plant Responses to Gibberellic Acid Treatment
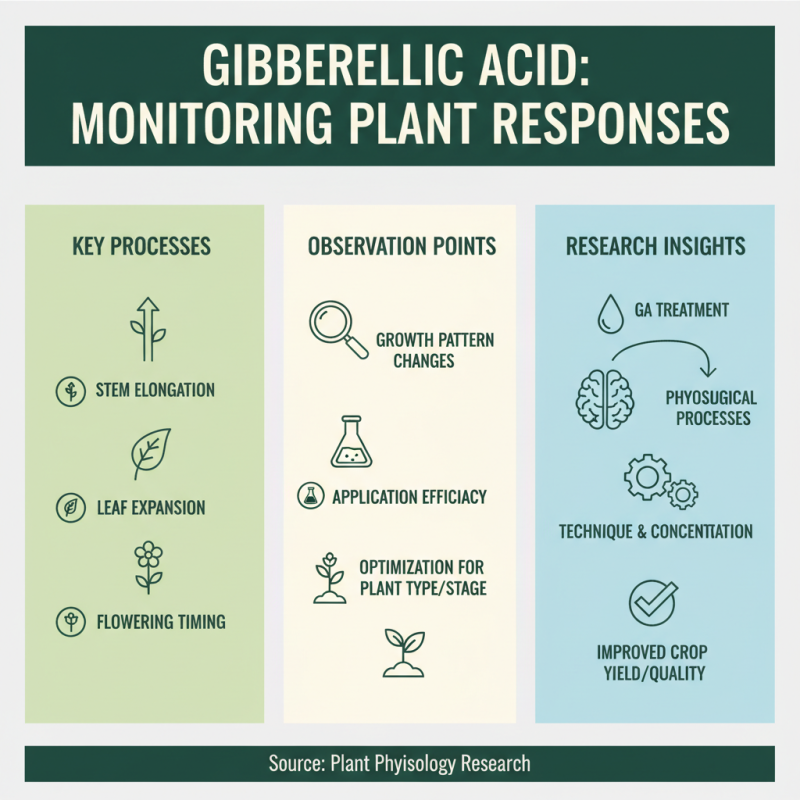
Monitoring plant responses to gibberellic acid treatment is crucial for understanding how this plant growth hormone influences various physiological processes. The application of gibberellic acid leads to notable alterations in growth patterns, including stem elongation, leaf expansion, and flowering timing. By observing these changes, researchers can gauge the efficacy of different application techniques and concentrations, thereby optimizing their use for specific plant types or growth stages.
To effectively monitor plant responses, various methods can be employed, such as measuring growth metrics, assessing leaf chlorophyll levels, and conducting visual assessments of plant vigor. Growth metrics like stem height, internode length, and leaf area provide quantitative data that can be tracked over time. Additionally, non-destructive techniques like chlorophyll fluorescence assessments can help evaluate how gibberellic acid influences photosynthetic efficiency and overall plant health. These observations not only inform the applicability of gibberellic acid in horticulture and agriculture but also contribute to a greater understanding of plant physiology under hormonal treatment.
Related Posts
-
Why Should You Consider Gibberellic Acid for Your Plant Growth Needs
-

Top 10 Uses of Gibberellic Acid in Plants for Increased Growth and Yield
-
Understanding Gibberellic Acid Label: Uses, Benefits, and Safety Information
-

How Gibberellic Acid Boosts Plant Growth: Benefits and Application Tips
-

How to Use Gibberellic Acid to Enhance Plant Growth Effectively
-

What is Gibberellic Acid and How to Use Gibberellic Acid Products Effectively
