site_4bbb466c-cafd-4edb-8869-71ed8e60d33a
Excellence in PGR technology
How to Use Gibberellic Acid for Plants Effectively in 2026
Gibberellic acid for plants is a powerful tool in horticulture. In 2026, its use has become more widespread. Experts emphasize its role in enhancing growth and flowering. Dr. Emily Carter, a leading plant biologist, states, “Gibberellic acid for plants can significantly boost crop yields when applied correctly.”
This growth regulator affects processes like seed germination, stem elongation, and fruit development. However, the challenge lies in its precise application. Too much gibberellic acid can lead to undesirable results, such as excessive stretch or poor fruit quality. Observation and adjustment are key when using this compound.
User experience is mixed. Some growers achieve remarkable outcomes, while others see minimal changes. It’s clear that gibberellic acid for plants requires careful consideration. Understanding plant responses is vital for effective use. Close monitoring is essential to avoid over-application and unintended consequences.

Understanding Gibberellic Acid: What It Is and Its Role in Plant Growth
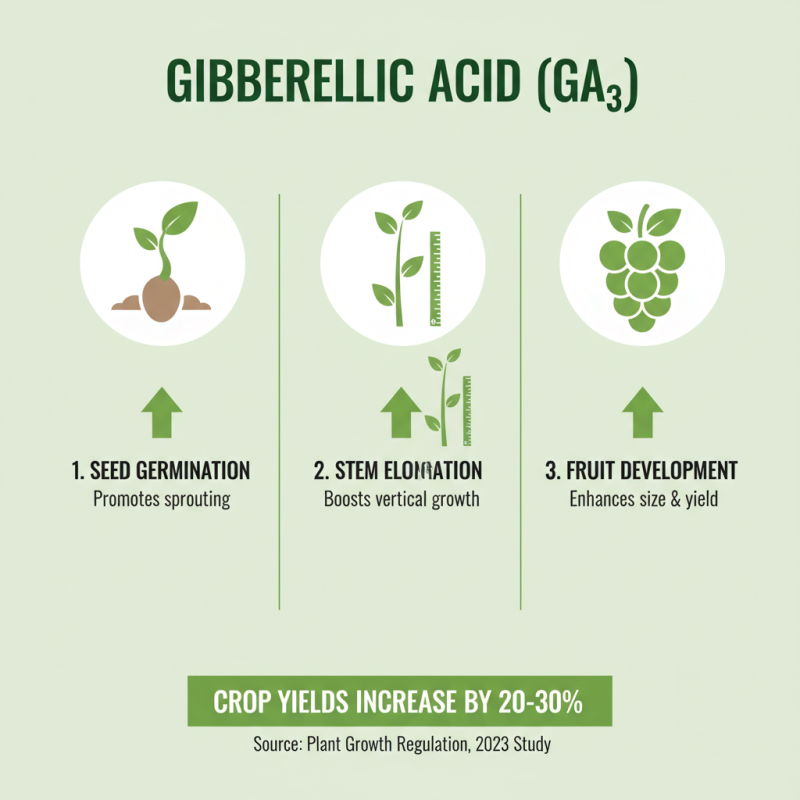
Gibberellic acid (GA3) is a plant hormone that plays a significant role in promoting growth and development. It's widely known for its ability to stimulate seed germination, elongate stems, and enhance fruit development. According to a 2023 study published in "Plant Growth Regulation," GA3 can increase crop yields by 20% to 30% when applied correctly. This makes it a valuable tool for growers looking to maximize their production.
Applying gibberellic acid requires precision. It’s crucial to determine the right concentration for your specific plants. Overuse can lead to undesired effects, such as excessive growth or weak stems. For best results, dilution is often recommended. A common safe recommendation is to start with a solution of 50 to 100 ppm and observe the results. Make adjustments as needed.
**Tips:**
- Test on a small area first.
- Monitor your plants closely after treatment.
- Consult recent agricultural journals for updated research.
Understanding the role of gibberellic acid can benefit all growers. Its correct application can lead to impressive results. However, growers should remain vigilant. Each plant species responds differently to GA3. Therefore, experimentation and observation are key to achieving optimal outcomes. Data indicates that growers should consider local climate and crop type when using gibberellic acid for better success.
Benefits of Gibberellic Acid Application for Various Plant Species
Gibberellic acid (GA) can bring numerous benefits to various plant species. This plant hormone influences growth, germination, and flowering. It promotes cell elongation, which can lead to taller plants and larger fruits. For some crops, it enhances seed germination rates significantly. Notably, it can also help break dormancy in certain seeds.
Applicators must take care, as too much GA can hinder growth. Overuse might result in weak stems or delayed flowering. Proper dosage is critical; not all plants respond the same way. Vegetables like tomatoes exhibit notable benefits from GA. Fruit trees may yield larger, more uniform fruit. However, certain species could be negatively affected. Understanding the specific needs of each plant is essential.
Timing is crucial in applying gibberellic acid. It should align with growth stages. Application too early or late might lead to poor results. Furthermore, environmental factors play a role. Temperature and humidity can affect how well plants respond. Observing plant reactions after application is vital for success. Careful monitoring can guide future usage, allowing farmers and gardeners to maximize their results.
Optimal Timing and Dosage for Applying Gibberellic Acid in 2026
Gibberellic acid can enhance plant growth when used correctly. Timing and dosage are crucial for effective application in 2026. Plants react differently depending on their growth stage. Early application can stimulate germination. For many plants, late winter to early spring is ideal.
Dosage varies by plant type and desired effect. Using too much can lead to excessive growth or weak stems. A common recommendation is 10 to 100 ppm. Monitoring is essential after application. Watch for signs of stress or overgrowth. Adjusting the dosage is key to achieving balanced growth.
Consider environmental factors. Temperature and humidity affect how plants absorb gibberellic acid. In dry or hot conditions, the effects may be intensified. Be cautious; every garden is unique. Keep detailed records of your application successes and failures. This can help refine your approach over time.
How to Use Gibberellic Acid for Plants Effectively in 2026 - Optimal Timing and Dosage
| Plant Type | Optimal Timing | Recommended Dosage (ppm) | Application Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tomatoes | Early Spring | 100-150 | Foliar Spray |
| Cucumbers | Mid Spring | 150-200 | Soil Drench |
| Apples | Pre-Bloom | 200-250 | Foliar Spray |
| Grapes | Mid Growing Season | 50-100 | Foliar Spray |
| Lettuce | Early Growth | 75-125 | Soil Drench |
Methods of Application: Foliar Spray vs. Soil Drench for Effectiveness

Gibberellic acid is a powerful growth hormone for plants. When deciding how to use it, two common methods come to mind: foliar spray and soil drench. Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses, and understanding these can improve your results.
Foliar spraying involves applying gibberellic acid directly to the leaves. This allows for quick absorption, leading to faster effects on plant growth. However, the spray must cover the leaf surface evenly. Over-saturation can cause runoff, wasting the product. Additionally, timing is crucial. Applying during the heat of the day may result in evaporation before absorption.
Soil drenching, on the other hand, delivers gibberellic acid directly to the roots. This method is effective for deep-rooted plants. The roots absorb the hormone, promoting healthy growth. Yet, it's easy to apply too much, leading to root saturation. Monitoring soil moisture is vital to avoid overwatering. Using the method incorrectly may yield disappointing results. Both methods require careful observation of your plants' responses.
Precautions and Potential Side Effects of Gibberellic Acid Usage in Horticulture
When using gibberellic acid in horticulture, it's crucial to understand potential side effects. This plant growth regulator can lead to excessive elongation of stems and leaves. If overapplied, plants may become weak and spindly. Finding the right balance is essential. Monitor your plants closely after treatment.
Another concern is the potential impact on flowering. Some plants may delay or reduce blooming when gibberellic acid is improperly administered. This could disrupt the growing cycle, leading to frustration in gardeners. Conducting small trials on a few plants can help determine the right dosage.
It’s also important to consider environmental factors. Temperature and humidity can affect absorption rates, leading to inconsistent results. Always adjust your approach based on local conditions. Keep in mind, every plant species responds differently; research is required. Thoughtful application can yield positive results, but caution is necessary to avoid unintended consequences.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Gibberellic Acid Uses in Plants You Should Know?
-

Top 10 Uses of Gibberellic Acid in Plants for Increased Growth and Yield
-

2025 How to Use Gibberellic Acid for Healthy Plant Growth
-
Gibberellic Acid for Plants Top Tips for Optimal Growth?
-

How to Effectively Use Gibberellic Acid Products for Plant Growth?
-
What is Gibberellic Acid Application in Agriculture?
