site_4bbb466c-cafd-4edb-8869-71ed8e60d33a
Excellence in PGR technology
Why Gibberellic Acid is Essential for Plant Growth and Development
Gibberellic acid, a crucial plant hormone, plays a significant role in various physiological processes that are vital for plant growth and development. Its discovery transformed our understanding of plant biology, highlighting the importance of hormones in influencing growth patterns and responses to environmental stimuli. The uses of gibberellic acid in plants are diverse, ranging from promoting seed germination to enhancing stem elongation and facilitating flowering. This naturally occurring compound has garnered substantial attention in both agricultural practices and horticultural applications, as it aids in maximizing plant productivity and improving crop yields.
As an essential component of plant growth-regulating strategies, gibberellic acid helps plants adapt to changing conditions and optimizes their developmental pathways. Through its various functions, it influences key growth stages, including internode elongation, seed development, and fruit set, thereby playing a pivotal role in agricultural efficiency. Understanding the mechanisms and applications of gibberellic acid is crucial for harnessing its potential in enhancing plant health and productivity. As researchers continue to explore the depth of gibberellic acid's influences, it is evident that this powerful hormone is not only vital for natural plant processes but also serves as a cornerstone for sustainable agricultural advancements.

Understanding Gibberellic Acid and Its Role in Plants
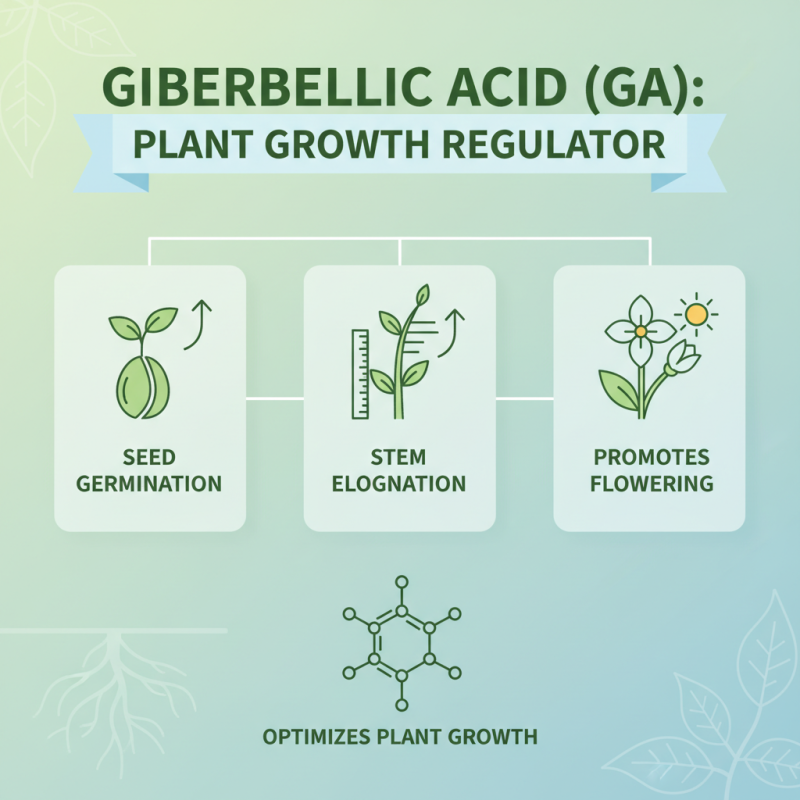
Gibberellic acid (GA) is a crucial plant hormone that plays a pivotal role in various aspects of plant growth and development. This naturally occurring compound belongs to a class of plant growth regulators known as gibberellins. Its primary functions include promoting stem elongation, seed germination, and flowering processes. By breaking dormancy in seeds and enhancing cell elongation, gibberellic acid enables plants to grow taller and more robust, effectively optimizing their access to sunlight and resources.
In addition to its influence on growth, gibberellic acid also coordinates the transition from vegetative to reproductive phases in plants. It regulates the timing of flowering and fruit development, ensuring that these processes occur under optimal environmental conditions. This hormone acts by stimulating the production of enzymes that break down food reserves during seed germination, allowing for the efficient mobilization of nutrients. As such, understanding the mechanisms of gibberellic acid provides valuable insights into agricultural practices and the enhancement of crop yields in a sustainable manner. Its multifaceted roles demonstrate its importance in plant biology and the overall health of ecosystems.
The Biosynthesis of Gibberellic Acid in Different Plant Species
Gibberellic acid (GA) is a crucial plant hormone that plays a significant role in regulating various growth processes, including seed germination, stem elongation, and fruit development. The biosynthesis of gibberellic acid occurs through a complex pathway that varies among different plant species, reflecting their unique physiological needs and environmental adaptations. In general, the biosynthesis begins with the conversion of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate into ent-kaurene, followed by a series of enzymatic transformations that ultimately lead to the formation of GA.
In monocots, such as rice and maize, gibberellic acid is synthesized primarily in young leaves and seeds, where active cell division and expansion are taking place. In contrast, many dicots, like peas and carrots, predominantly produce GA in their stems and roots. The variations in biosynthetic pathways are influenced by specific enzymes and regulatory genes present in each species, which determine the efficiency and rate of gibberellin production.
Furthermore, external environmental factors such as light, temperature, and water availability can also modulate the expression of genes involved in GA biosynthesis, showcasing the dynamic interaction between plants and their environments.
Mechanisms of Action: How Gibberellic Acid Influences Plant Growth
Gibberellic acid (GA) is a vital plant hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating various growth processes. One of the primary mechanisms of action of gibberellic acid is its capacity to promote stem elongation. GA breaks down the cell walls, enhancing cell growth and division, which results in longer internodes. This elongation is particularly evident in plants that exhibit dwarfism due to genetic mutations affecting gibberellin production. By applying gibberellic acid, these plants can achieve normal height and vigor, showcasing the hormone’s power in overcoming growth restrictions.
Moreover, gibberellic acid is instrumental in seed germination and fruit development. During germination, GA stimulates the production of enzymes that break down the starches stored in seeds, making nutrients available for the growing plant. It also plays a role in the transition from vegetative growth to flowering, influencing flowering time and fruit set. The ability of gibberellic acid to regulate such critical phases of development highlights its significance in agricultural practices, where controlling plant height and promoting uniform ripening can lead to higher yields and better-quality produce. Thus, understanding these mechanisms is essential for harnessing the full potential of gibberellic acid in plant cultivation.
Why Gibberellic Acid is Essential for Plant Growth and Development - Mechanisms of Action
| Mechanism of Action | Effect on Plant Growth | Examples of Impacted Processes | Applications in Agriculture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Promotes Stem Elongation | Increases height and improves light capture | Cell division and elongation | Used in grains for taller plants and higher yield |
| Enhances Seed Germination | Speeds up the sprouting process | Breaks dormancy of seeds | Used in horticulture for uniform germination |
| Stimulates Flowering | Improves flower production and quality | Induces flowering in certain plants | Used in fruit trees to increase yield |
| Imitates Effects of Light | Enhances photosynthesis and growth | Promotes chlorophyll synthesis | Applied in shaded areas to increase productivity |
| Regulates Fruit Development | Affects size, color, and ripening of fruits | Facilitates seedless fruit formation | Widely used in vineyards and orchards |
Effects of Gibberellic Acid on Seed Germination and Stem Elongation
Gibberellic acid (GA) plays a pivotal role in promoting seed germination and facilitating stem elongation in plants. During seed germination, GA triggers a cascade of physiological changes that lead to the breaking of dormancy. It activates enzymes such as α-amylase, which breaks down stored starches into sugars, providing the necessary energy for the growing embryo. This process is crucial, as it not only boosts the initial growth of the seedling but also enhances its overall vigor, setting a strong foundation for future development.
Furthermore, gibberellic acid is essential for stem elongation, particularly during the early stages of a plant's life. By promoting cell elongation and division, GA helps the plant grow taller and stronger, improving its ability to reach sunlight and access other resources. This elongation is especially important in competitive environments where light is a limiting factor. The regulated application of gibberellic acid enables plants to achieve optimal height and structural integrity, thus improving their adaptability and survival in diverse habitats. As a result, understanding and utilizing gibberellic acid's effects on these key growth processes can significantly enhance agricultural practices and plant development strategies.
Effects of Gibberellic Acid on Seed Germination and Stem Elongation
Applications of Gibberellic Acid in Agriculture and Horticulture
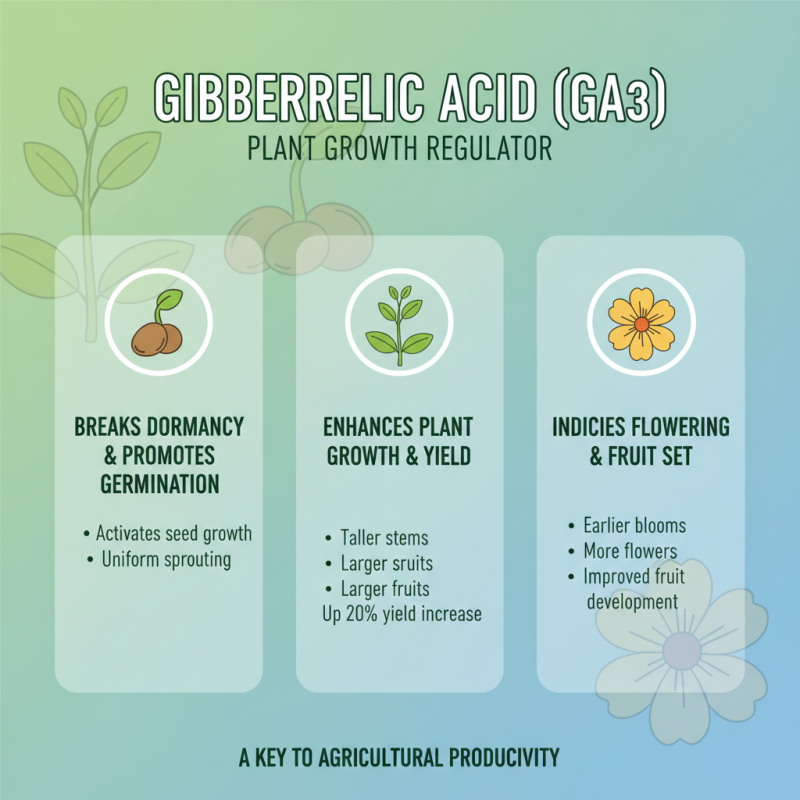
Gibberellic acid (GA3) plays a crucial role in agricultural and horticultural practices due to its unique properties that regulate plant growth and development. This plant hormone is particularly effective in breaking dormancy, promoting seed germination, and enhancing flowering in various crops. According to a report by the International Fertilizer Industry Association, the application of gibberellic acid can increase yields by up to 20% in certain crops, making it an invaluable tool for farmers seeking improved productivity.
In commercial horticulture, GA3 is widely used to manipulate flowering times and fruit development. For example, studies have shown that applying gibberellic acid can significantly increase the size and quality of fruits such as grapes and apples. A USDA report indicates that treated grapes have exhibited up to a 30% increase in berry size, reflecting not only the efficiency of GA3 but also its importance in meeting market demands for high-quality produce. Additionally, it aids in the thinning of fruits, allowing for better nutrient distribution among fewer fruits, ultimately leading to enhanced quality and marketability.
Furthermore, GA3 has been identified as a vital agent in increasing the robustness of plants against environmental stresses. Research published in the journal 'Plant Growth Regulation' suggests that when plants are treated with gibberellic acid, their resilience to drought conditions improves, resulting in healthier crops during unfavorable weather patterns. This characteristic is especially relevant as climate change continues to challenge agricultural sustainability, reinforcing the essential role of gibberellic acid in modern farming and horticultural practices.
Related Posts
-

How Gibberellic Acid Boosts Plant Growth: Benefits and Application Tips
-

Top 10 Uses of Gibberellic Acid in Plants for Increased Growth and Yield
-

How to Use Gibberellic Acid to Enhance Plant Growth Effectively
-

What is Gibberellic Acid and How to Use Gibberellic Acid Products Effectively
-

Top Benefits of Gibberellic Acid in South Africa for Enhanced Crop Growth
-

Effective Gibberellic Acid Application Techniques for Maximum Plant Growth
